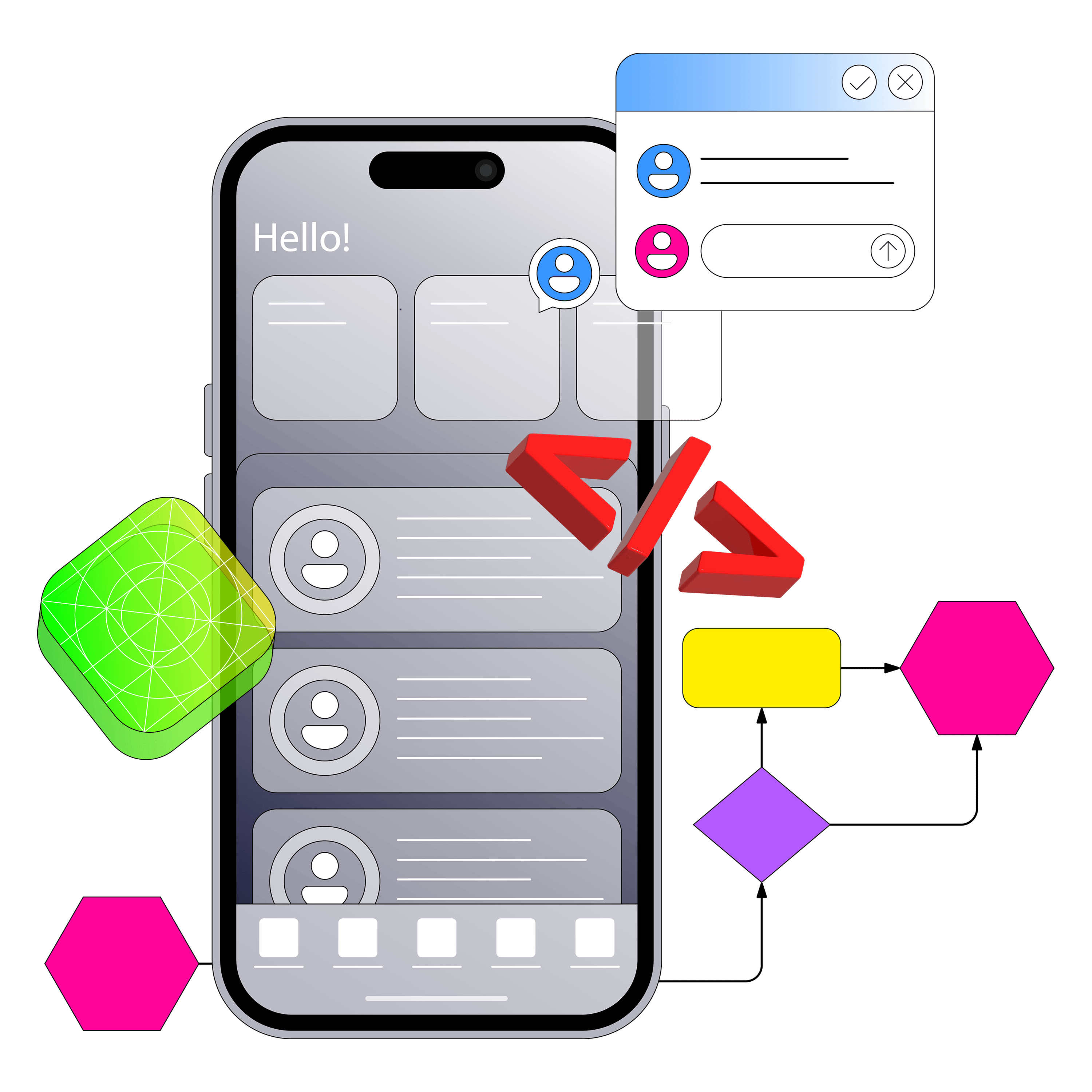
In a world where more than 3.8 billion people now access the internet through smartphones, delivering a fast, secure, and modern mobile experience is no longer optional—it’s the baseline for staying competitive. Whether you’re a startup founder, a CTO leading digital transformation, or a product manager mapping out the next big release, this Ultimate Guide to Custom Mobile App Development covers everything you need to know. We’ll walk through how to choose the right development frameworks (native vs. cross-platform), where AI in app development makes the biggest impact, what to consider when hiring developers and evaluating salaries, and why app permission settings and security should never be an afterthought. By the end, you’ll have clear insights on how to build a scalable, secure, and user-first app—one that wows users, ranks well in app stores, and drives real business growth.
What Is Custom Mobile App Development?
Custom Mobile App Development is the process of creating applications tailored precisely to your business goals, customer needs, and technical requirements—far beyond what ready-made or template-based solutions can deliver.
Here’s why brands choose custom development over “cookie-cutter” apps:
Bespoke UX/UI vs. Templates
Instead of cramming your identity into pre-built layouts, custom apps give you full control over design, interactions, and user journeys. Every screen and animation can reinforce your unique brand experience.
Performance & Scalability
Custom architecture ensures faster load times, smoother updates, and robust offline capabilities. As your user base grows, the app scales gracefully—critical for high-traffic businesses.
Strategic Differentiation
With AI-powered personalization, native device integrations, or advanced in-app security controls, your app builds a competitive moat that’s hard for rivals to copy.
Business Benefits at a Glance
- Speed to Market: Streamlined pipelines get your idea into users’ hands faster.
- Cost Efficiency Over Time: Maintainable codebase and fewer third-party tool dependencies lower long-term costs.
- Enhanced ROI: Features built specifically for your target audience improve retention and monetization.
Top Frameworks & Cross-Platform Services
Selecting the right framework is pivotal. Below are the five leading options—each with unique strengths for different project needs.
Framework | Language/Tech | Ideal Project Type |
Flutter (Google) | Dart | Rich custom UI across mobile, web, desktop |
React Native (Meta) | JavaScript/React | Fast prototyping with large community support |
Xamarin / .NET MAUI (Microsoft) | C#/.NET | Enterprise-grade apps, deep Azure integration |
PWAs & Hybrid (Cordova/Ionic) | HTML/CSS/JS | Content-driven or simple functionality apps |
Kotlin Multiplatform (JetBrains) | Kotlin | Share core logic while retaining native UIs |
2.1 Flutter
- Key Features: Single Dart codebase for iOS, Android, Web, Windows, macOS & Linux.
- Pros: Near-native performance, expressive widgets, hot-reload speeds debugging.
- Cons: Learning curve for Dart, occasional plugin limitations on web.
- Best For: Apps requiring a highly bespoke UI across all form factors.
2.2 React Native
- Key Features: JavaScript/React syntax, vast npm ecosystem.
- Pros: Rapid development, easy onboarding for web developers.
- Cons: Bridge-based architecture can introduce latency; complex modules may need native code.
- Best For: MVPs, apps with moderate UI complexity needing fast iteration.
2.3 Xamarin / .NET MAUI
- Key Features: C#/.NET single codebase, native UI controls, tight Microsoft ecosystem integration.
- Pros: Enterprise support, seamless Azure services, true native look and feel.
- Cons: Larger binary sizes, macOS support still maturing.
- Best For: Large enterprises already invested in Microsoft stack.
2.4 PWAs & Hybrid (Cordova/Ionic)
- Key Features: Leverage web technologies—HTML, CSS, JavaScript—for mobile and web.
- Pros: Rapid prototyping, web-first codebase.
- Cons: Not ideal for animation-heavy or resource-intensive apps, UX can feel less “native.”
- Best For: Content-centric apps, internal enterprise tools, or simple utility apps.
2.5 Kotlin Multiplatform (KMP)
- Key Features: Share business logic in Kotlin across Android, iOS, Desktop, and Web.
- Pros: True code sharing for core modules, progressively maturing Compose Multiplatform for UI.
- Cons: UI sharing still evolving; teams need expertise in native UI frameworks.
- Best For: Projects prioritizing shared core logic with highly customized native interfaces.
AI in App Development: Emerging Trends
AI isn’t just a buzzword—it’s a productivity turbocharger and a user-experience enhancer. Here are three game-changing AI tools transforming the developer workflow:
3.1 Google Gemini
- Integration: Deeply embedded in Android Studio and via Firebase AI SDK for both Android and iOS.
- Capabilities: Auto-generate variable/method names, XML layouts, Jetpack Compose UI, unit tests, and even commit messages.
- Benefit: Cuts boilerplate coding time by up to 30%, empowers developers to focus on business logic and UX.
3.2 GitHub Copilot
- Integration: Works in VS Code, JetBrains IDEs, and other editors.
- Capabilities: Context-aware code completions—from single lines to full classes. Supports JavaScript, Kotlin, Swift, Dart, C#, and more.
- Benefit: Slashes development cycles by suggesting tested, idiomatic code snippets instantly.
3.3 ChatGPT & Claude AI
- Usage: Accessible via web or API rather than direct IDE plugins.
- Capabilities: Generate boilerplate code, troubleshoot bugs from stack traces, design high-level architectures (“What’s the best offline-first chat architecture?”).
- Benefit: Ideal for early-stage exploration and brainstorming—just remember to review and refactor generated code for production quality.
Real-World Impact: Company X used Copilot and Gemini together to reduce front-end development time by 30%, enabling them to ship two major feature releases within three months instead of six.
Hiring & Developer Salaries: Building Your Dream Team
4.1 Key Roles & Responsibilities
- Front-End Developers (Flutter, React Native): Craft UI/UX, animations, and cross-platform consistency.
- Back-End Developers (Node.js, .NET, Kotlin MPP): Architect APIs, databases, and server logic.
- DevOps Engineers: Automate CI/CD pipelines, infrastructure provisioning, and monitoring.
- QA & Test Automation Engineers: Ensure reliability across dozens of devices and OS versions.
4.2 Global Salary Benchmarks (2025)**
| Role | India (₹ LPA) | US (USD) | Europe (€) |
| Flutter / React Native Dev | 8–15 LPA | 80–110 k | 60–85 k |
| Kotlin / Swift Mobile Dev | 10–18 LPA | 90–130 k | 70–95 k |
| Full-Stack / DevOps Engineer | 12–20 LPA | 100–140 k | 75–110 k |
| QA / Test Automation | 6–12 LPA | 70–100 k | 50–75 k |
4.3 Vetting Candidates
- Portfolio Reviews: Look for apps in stores with real-world user feedback.
- Live Coding Tests: Include AI-code challenge scenarios to assess how they integrate Copilot/Gemini responsibly.
- Soft Skills: Communication, collaboration, and agile mindset are as crucial as technical prowess.
App Permission Settings & Security Best Practices
5.1 Minimize & Contextualize Permissions
- Limit Requests: Only ask for strictly necessary permissions (e.g., camera, location).
- Delay Prompts: Trigger permission dialogs right before the action (e.g., opening the gallery), not on first launch.
- Selective Media Access (iOS): For photo selection, request single-image access rather than full library.
5.2 Handle Denials Gracefully
- Explain Limitations: If a user denies a permission, show why a feature is limited and suggest alternative workflows.
- Fallback Options: Disable related features or guide users to app settings (Android: intent to settings; iOS: manual settings prompt).
5.3 Transparency & Ongoing Indicators
- Clear Messaging: Always specify why you need each permission and how data will be used.
- Active Use Indicators: Show an on-screen icon when hardware like the microphone or camera is active.
5.4 Cross-Platform & Regulatory Compliance
- Consistent Testing: Verify permission flows across Android 6–14+ (various OEMs) and iOS privacy models.
- Encryption & Secure CI/CD: Encrypt sensitive data at rest and in transit. Embed OWASP Mobile Top 10 checks into your pipeline.
- Stay Updated: Regularly review OS privacy changes and update prompts to comply with GDPR, CCPA, and platform policies.
Why It Matters:
- User Trust & Retention: Over-asking or nagging drives uninstalls.
- Platform Approval: Non-compliance risks app rejection or removal.
- Competitive Edge: Users value transparency and control—differentiators in crowded app stores.
Conclusion
Custom Mobile App Development is more than just building a product—it’s your gateway to unparalleled user engagement, streamlined operations, and sustainable business growth.
By carefully choosing the right frameworks, integrating AI in app development, hiring skilled developers at competitive salaries, and enforcing strong app permission settings and security, you can create an app that does more than function—it inspires loyalty, stands out in the market, and fuels long-term revenue expansion.
Ready to Turn Your Vision Into Reality?
Partner with Drish Infotech’s expert team for end-to-end custom mobile app development. From AI-driven personalization to enterprise-grade security and scalable frameworks, we deliver solutions built to last.